Abstract It is commonly accepted that mitochondria represent a major source of free radicals following acute brain injury or during the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. The levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells are determined by two opposing...
Brain Damage
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) Research for Brain Damage.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for mild traumatic brain injury persistent postconcussion syndrome: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract: Persistent postconcussion syndrome (PPCS) after mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) is a significant public health and military problem for which there is limited treatment evidence. The aim of this study was to determine whether forty 150 kPa hyperbaric...
Management of Concussion and Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Synthesis of Practice Guidelines
Abstract At least 3 million Americans sustain a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) each year, and 1 in 5 have symptoms that persist beyond 1 month. Standards of mTBI care have evolved rapidly, with numerous expert consensus statements and clinical practice guidelines...
High-Dose Intravenous Ascorbic Acid: Ready for Prime Time in Traumatic Brain Injury?
Abstract Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the leading public health problems in the USA and worldwide. It is the number one cause of death and disability in children and adults between ages 1-44. Despite efforts to prevent TBIs, the incidence continues to rise....
The role of pulsed magnetic fields in the management of concussion and traumatic brain injury
Abstract Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a complex clinical phenomenon. (Raji) The classic designations of mild, moderate, or severe TBI are based on the acute clinical presentation and do not necessarily predict the long-term outcome. The long held assumption that...
Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury With Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
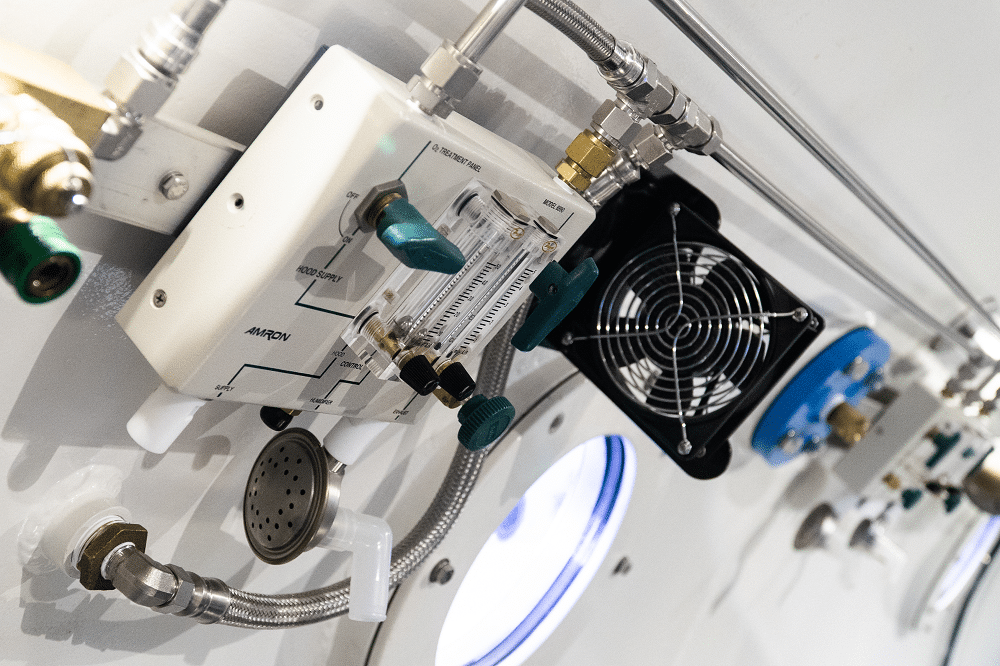
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is defined as the use of oxygen at higher than atmospheric pressure for the treatment of underlying disease processes and the diseases they produce. Modern HBOT in which 100% O2 is breathed in a pressurized chamber dates back to the 1930s, when it was first used for treatment of decompression illness in divers. There are currently 13 FDA-approved uses for HBOT, including decompression illness, gas gangrene, air embolism, osteomyelitis, radiation necrosis, and the most recent addition—diabetic ulcers. HBOT can dramatically and permanently improve symptoms of chronic TBI months or even many years after the original head injury. This assertion is generally met with skepticism within the medical establishment because we have been taught for generations that any post-concussion symptoms persisting more than 6 months or so after a head injury are due to permanent brain damage that cannot be repaired.
The National Brain Injury Rescue and Rehabilitation Study – a multicenter observational study of hyperbaric oxygen for mild traumatic brain injury with post-concussive symptoms
The National Brain Injury Rescue and Rehabilitation Project was established as a preliminary study to test the safety and practicality of multi-center hyperbaric oxygen administration for the post-concussive symptoms of chronic mild traumatic brain injury as a precursor to a pivotal, independent, multi-center, controlled clinical trial. This report presents the results for 32 subjects who completed a preliminary trial of hyperbaric oxygen several years before the passage of the 21 st Century Cures Act. This study anticipated the Act and its reassessment of clinical research. Subjects received 40-82 one-hour treatments at 1.5 atmospheres absolute 100% oxygen. Outcome measures included repeated self-assessment measures and automated neurocognitive tests. The subjects demonstrated improvement in 21 of 25 neurocognitive test measures observed. The objective neurocognitive test components showed improvement in 13 of 17 measures. Earlier administration of hyperbaric oxygen post injury, younger age at the time of injury and hyperbaric oxygen administration, military status, and increased number of hyperbaric oxygen administrations were characteristics associated with improved outcomes. There were no adverse events. Hyperbaric oxygen was found to be safe, inexpensive and worthy of clinical application in the 21 st Century model of facile data collection provided by recent research regulatory shifts in medicine. The study was approved by the ethics review committee of the Western Institutional Review Board (WIRB; Protocol #20090761).
Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury
Despite the increased public awareness of traumatic brain injury (TBI), the complexities of the neuropsychiatric, neuropsychological, neurological, and other physical consequences of TBI of all severities across the lifespan remain incompletely understood by patients,...
Erratum: Effect of hyperbaric oxygenation therapy on post-concussion syndrome.
The present review evaluated the effect of hyperbaric oxygenation (HBO) therapy on post-concussion syndrome (PCS). Searches for publications from the earliest date possible up until the first week of 2016 were conducted using the electronic databases Cochrane, EBSCOhost, Embase, Ovid MEDLINE, PubMed and Web of Science. Additional trials were identified through reference list scanning. Randomized controlled trials assessing the effectiveness of HBO therapy in PCS were selected and tested for eligibility for inclusion in the present review.