Abstract Objectives: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. In quantified EEG (qEEG), the AD patients have a greater amount of theta activity compared with normal elderly individuals. Little is known about the effect of neurofeedback in patients...
Dementia
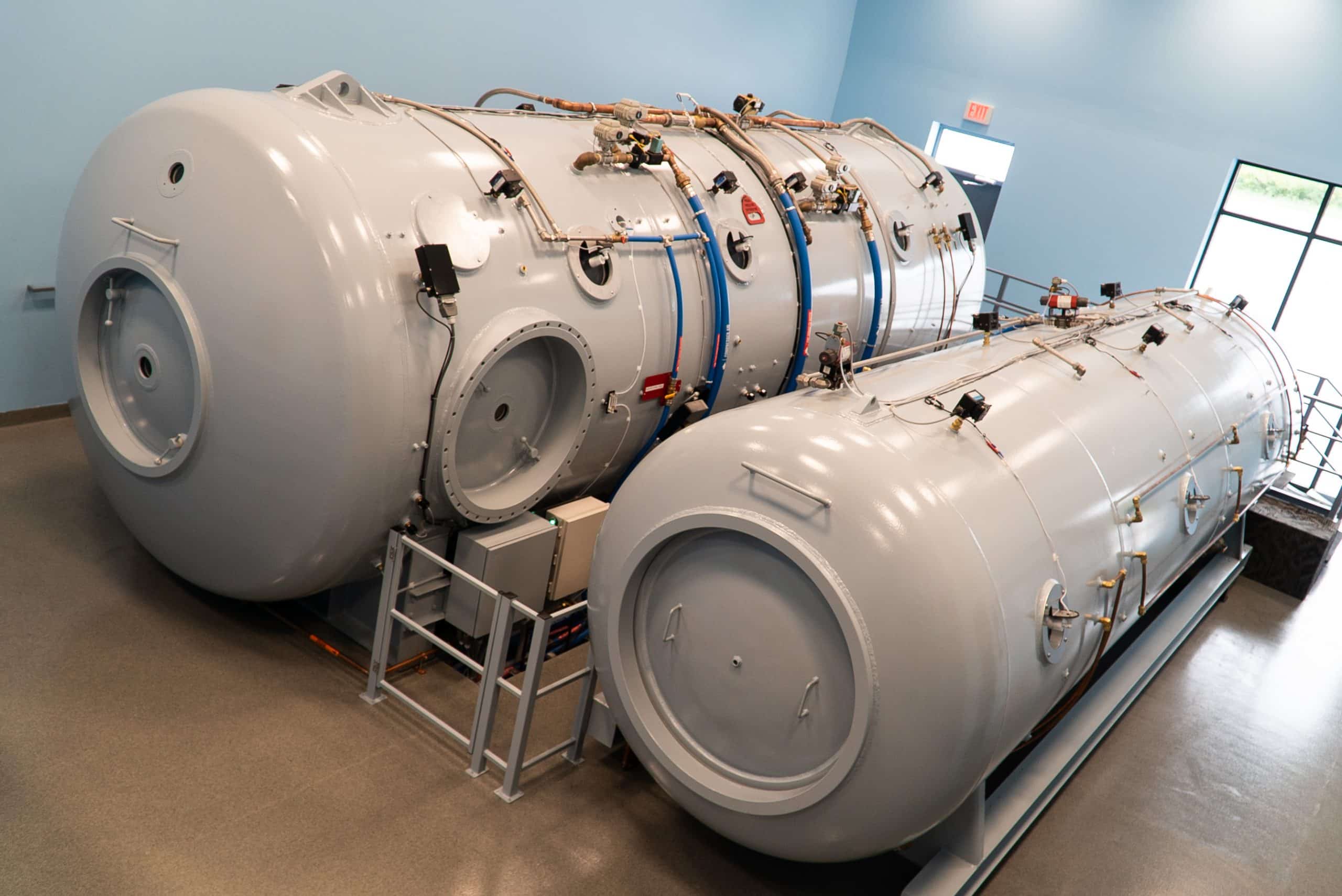
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) Research for Dementia.
Hyperbaric oxygen may induce angiogenesis in patients suffering from prolonged post-concussion syndrome due to traumatic brain injury.
Abstract Purpose: Recent clinical studies present convincing evidence that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) may be the coveted neurotherapeutic method for brain repair. One of the most interesting ways in which HBOT can induce neuroplasticity is angiogenesis. The...
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: an introduction
Abstract Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has a rich and diverse history, both in the United States and around the world. From its early uses in war to the building of bridges, and through many introductions to innovations in the medical community, it has been debated and...
Humanin: a harbinger of mitochondrial-derived peptides?
Abstract Mitochondria have been largely considered as 'end-function' organelles, servicing the cell by producing energy and regulating cell death in response to complex signals. Being cellular entities with vital roles, mitochondria communicate back to the cell and...
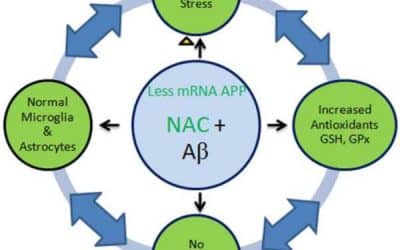
Elevation of glutathione as a therapeutic strategy in Alzheimer disease
Abstract Oxidative stress has been associated with the onset and progression of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer disease (AD). AD and MCI brain and plasma display extensive oxidative stress as indexed by protein oxidation, lipid peroxidation, free radical...
Hyperbaric oxygen – its mechanisms and efficacy
Principal mechanisms of HBO2 are based on intracellular generation of reactive species of oxygen and nitrogen. Reactive species are recognized to play a central role in cell signal transduction cascades and the discussion will focus on these pathways. Systematic reviews and randomized clinical trials support clinical use of HBO2 for refractory diabetic wound healing and radiation injuries; treatment of compromised flaps and grafts and ischemia-reperfusion disorders is supported by animal studies and a small number of clinical trials, but further studies are warranted.
Electroencephalographic rhythms in Alzheimer’s disease
Abstract Physiological brain aging is characterized by synapses loss and neurodegeneration that slowly lead to an age-related decline of cognition. Neural/synaptic redundancy and plastic remodelling of brain networking, also due to mental and physical training,...
Magnesium in Alzheimer’s disease
Excerpt Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. It is characterized by a progressive cognitive impairment clinically, and excessive deposits of aggregated amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides pathologically. Environmental factors, including nutrition and...
EEG neurofeedback: a brief overview and an example of peak alpha frequency training for cognitive enhancement in the elderly
Abstract Neurofeedback (NF) is an electroencephalographic (EEG) biofeedback technique for training individuals to alter their brain activity via operant conditioning. Research has shown that NF helps reduce symptoms of several neurological and psychiatric disorders,...