Abstract Background: Psoriasis is sustained by pro-inflammatory CD4+ T helper cells mainly belonging to the Th1, Th17 and Th22 lineage. Objective: To identify whether treatment with the anti-tumour-necrosis-factor antagonist etanercept is able to induce significant...
Psoriasis
Therapeutic effect of hyperbaric oxygen in psoriasis vulgaris: two case reports and a review of the literature.
Abstract: Psoriasis is an inflammatory and immunological cutaneous disease. The high morbidity in patients with psoriasis results from severe clinical manifestations and/or adverse effects of treatment. The Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society and Federal Medicare...
Low frequency and low intensity pulsed electromagnetic field exerts its anti-inflammatory effect through restoration of plasma membrane calcium ATPase activity
Abstract Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting 1% of the population worldwide. Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) has a number of well-documented physiological effects on cells and tissues including antiinflammatory effect. This study...
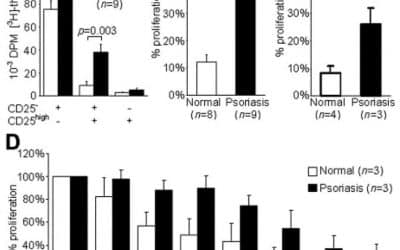
Dysfunctional blood and target tissue CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in psoriasis: mechanism underlying unrestrained pathogenic effector T cell proliferation
Abstract The balance between regulatory and effector functions is important for maintaining efficient immune responses, while avoiding autoimmunity. The inflammatory skin disease psoriasis is sustained by the ongoing activation of pathogenic effector T cells. We found...
The role of oxidants and antioxidants in psoriasis
Abstract Background: Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by well-demarcated erythema and scaly plaques. The pathogenesis of psoriasis still remains unclear. An increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and insufficient antioxidant...