Abstract Objective To investigate the effectiveness of alpha activity neurofeedback training over the parietal lobe in GAD patients. Methods Twenty‐six female patients who had been diagnosed as GAD according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental...
Neurofeedback
Denver First Responders Find Relief From Job-Related Trauma With Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback has been able to relieve first responders of PTSD, job burnout, and suicidal thoughts. The job of a first responder is nothing short of honorable, but after years of seeing traumatic scenes and helping people on the worst days of their lives, it can...
A Neurofeedback Protocol for Executive Function to Reduce Depression and Rumination: A Controlled Study
Abstract Objective: Rumination is a maladaptive emotional-regulation strategy that is strongly associated with depression. Impaired executive function can lead to difficulties in disengaging from rumination, thus exacerbating depression. In this study, we inspect an...
Neurofeedback Treatments Rated Effective in ADHD
Neurofeedback treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) demonstrate medium to large effect sizes and remission rates between 32% and 47%, according to a study published online in the journal Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. “Standard neurofeedback protocols in the treatment of ADHD can be concluded to be a well-established treatment, or ‘efficacious and specific’ in line with the American Psychological Association guidelines,” researchers wrote.
The Effectiveness of Neurofeedback Therapy as an Alternative Treatment for Autism Spectrum Disorders in Children: A Systematic Review
Abstract Findings for the effectiveness of neurofeedback in autism spectrum disorder are found to be inconsistent. Therefore, this review comprehensively and systematically reviewed literature on the effectiveness of neurofeedback for the treatment of autism spectrum...
Role of oxidative stress in depression
Abstract Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have vital roles in cellular signaling and in defence against invasive microorganisms. Excessive ROS generation and exhaustion of antioxidative defences trigger proinflammatory signaling, damaging vital macromolecules and...
Self-Regulation of SMR Power Led to an Enhancement of Functional Connectivity of Somatomotor Cortices in Fibromyalgia Patients
Abstract Neuroimaging studies have demonstrated that altered activity in somatosensory and motor cortices play a key role in pain chronification. Neurofeedback training of sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) is a tool which allow individuals to self-modulate their brain...
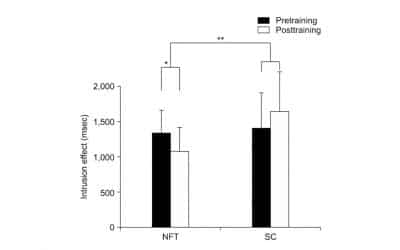
Beta Neurofeedback Training Improves Attentional Control in the Elderly
Abstract One of the well-documented behavioral changes that occur with advancing age is a decline in executive functioning, for example, attentional control. Age-related executive deficits are said to be associated with a deterioration of the frontal lobes....
Comparing the Effectiveness of Neurofeedback and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Sleep Quality of Patients With Migraine
Abstract Introduction: Migraine is considered one of the most common primary headache disorders. Migraine attacks may occur due to a lack of sleep. Furthermore, sleep is regarded as one of the smoothing factors of migraine pain. Patients with sleep disorders often...