HBOT Research
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is increasingly appearing in new research as a treatment for a variety of conditions involving inflammation. Use the search or select an article below to to keep up to date on the most recent HBOT Research.
Recent Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) Research
The Use of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields to Promote Bone Responses to Biomaterials In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract Implantable biomaterials are extensively used to promote bone regeneration or support endosseous prosthesis in orthopedics and dentistry. Their use, however, would benefit from additional strategies to improve bone responses. Pulsed...
[HYPERBARIC OXYGEN THERAPY (HBO) FOR RADIATION NECROSIS – PHYSICIAN AWARENESS IS REQUIRED].
Abstract: Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy is the inhalation of 100% oxygen at a pressure of at least 1.4 atmospheres absolute (ATA), 140 kPa, in the hyperbaric chamber. The therapeutic effect is obtained by delivery of oxygen to the tissues...
[HYPERBARIC OXYGEN TREATMENT FOR POST RADIATION NECROSIS].
Abstract: Radiation therapy is an acceptable treatment for several types of malignancies. Despite advances in technology, the adverse effects of radiation therapy are still common. Tissue radio necrosis/post radiation necrosis is a frequent adverse...
The Multiple Applications and Possible Mechanisms of the Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy.
Abstract: Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy (HBOT) is used as adjunctive method for multiple diseases. The method meets the routine treating and is non-invasive, as well as provides 100% pure oxygen (O2) which is at above-normal atmospheric pressure...
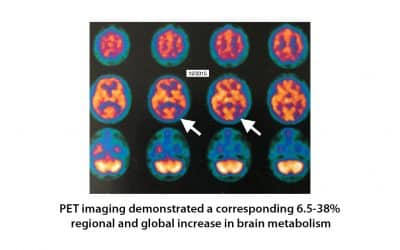
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for Alzheimer’s dementia with positron emission tomography imaging: a case report.
A 58-year-old female was diagnosed with Alzheimer’s dementia (AD) which was rapidly progressive in the 8 months prior to initiation of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) brain imaging demonstrated global and typical metabolic deficits in AD (posterior temporal-parietal watershed and cingulate areas). An 8-week course of HBOT reversed the patient’s symptomatic decline. Repeat PET imaging demonstrated a corresponding 6.5-38% regional and global increase in brain metabolism, including increased metabolism in the typical AD diagnostic areas of the brain.
[The influence of hyperbaric oxygenation on the elastic properties of platelet membrane during spontaneous platelet aggregation in the patients presenting with cardiac co-morbidity].
Abstract: The authors present evidence of the significance and role of the disturbances in platelet hemostasis in pathogenesis of co-morbid cardiac pathology and the absence of the unambiguous opinion as regards the expediency of the application of...
A Rare Case of Cerebral Air Embolism Caused by Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformation After Removal of a Central Venous Catheter.
Abstract: Cerebral air embolism following central venous catheter (CVC) removal is extremely rare. We report a case of cerebral air embolism with loss of consciousness after removal of CVC caused by pulmonary arteriovenous malformation (PAVM)....
Predictors of mortality after extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Abstract: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a promising adjunct to cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) in refractory cardiac arrest (CA). Factors associated with outcome are incompletely characterised. The aim of our study was to...
Evaluation of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for spinal cord injury in rats with different treatment course using diffusion tensor imaging.
Animal study. To evaluate the efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy for spinal cord injury (SCI) in rats with different treatment course using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Hospital in Fuzhou, China. Fifty adult Sprague-Dawley rats were grouped as: (A) sham-operated group (n = 10); (B) SCI without HBO therapy group (n = 10); (C) SCI with HBO therapy for 2 weeks (SCI+HBO) group (n = 10); (D) SCI with HBO therapy for 4 weeks (SCI+HBO) group (n = 10); (E) SCI with HBO therapy for 6 weeks (SCI+HBO) group (n = 10). Basso Beattie Bresnahan (BBB) scores and diffusion tensor imaging parameters including fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), radial diffusion (RD), and axial diffusion (AD) values in the injury epicenter, as well as 2 mm rostral and caudal to the injury epicenter were collected and analyzed 6 weeks post-injury.